NEWS
Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye'
-
@jan1 said in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Zwei Jahr mit Pi auf SD Karte und keine defekt
Fahre übrigens auch schon zwei Jahre mit 'nem Karren :car::zzz: und der fährt immer noch! Da leuchtet zwar ein Service/Werkstatt Lämpchen und irgendwelche Fehler mit Einspritzung und ein anderer bezüglich Luftfilter werden angezeigt, aber er fährt! Und der blaue Rauch aus dem Auspuff stört mich eigentlich auch nur wenn ich an der Ampel stehe ;)
:arrow_forward: Your mileage may vary :bulb:
von den apokalyptischen Szenarien
Um welche Szenarien handelt es sich denn da genau? :eyes:
-
@jan1 said in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Zwei Jahr mit Pi auf SD Karte und keine defekt
Fahre übrigens auch schon zwei Jahre mit 'nem Karren :car::zzz: und der fährt immer noch! Da leuchtet zwar ein Service/Werkstatt Lämpchen und irgendwelche Fehler mit Einspritzung und ein anderer bezüglich Luftfilter werden angezeigt, aber er fährt! Und der blaue Rauch aus dem Auspuff stört mich eigentlich auch nur wenn ich an der Ampel stehe ;)
:arrow_forward: Your mileage may vary :bulb:
von den apokalyptischen Szenarien
Um welche Szenarien handelt es sich denn da genau? :eyes:
@opensourcenomad sagte in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Zwei Jahr mit Pi auf SD Karte und keine defekt
Fahre übrigens auch schon zwei Jahre mit 'nem Karren :car::zzz: und der fährt immer noch! Da leuchtet zwar ein Service/Werkstatt Lämpchen und irgendwelche Fehler mit Einspritzung und ein anderer bezüglich Luftfilter werden angezeigt, aber er fährt! Und der blaue Rauch aus dem Auspuff stört mich eigentlich auch nur wenn ich an der Ampel stehe ;)
Naja, hoffe das ist mit Ironie behaftet sonst hinkt der Vergleich schon arg.
Am Pi leuchtet kein Lämpchen, es qualmt nichts und es gibt auch erstmal keine Fehler.
Es kann lediglich passieren das unter bestimmten Konstellation die SD Karte einen Schaden nimmt.
Das passt zu deinem Auto Beispiel null.
-
@opensourcenomad sagte in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Zwei Jahr mit Pi auf SD Karte und keine defekt
Fahre übrigens auch schon zwei Jahre mit 'nem Karren :car::zzz: und der fährt immer noch! Da leuchtet zwar ein Service/Werkstatt Lämpchen und irgendwelche Fehler mit Einspritzung und ein anderer bezüglich Luftfilter werden angezeigt, aber er fährt! Und der blaue Rauch aus dem Auspuff stört mich eigentlich auch nur wenn ich an der Ampel stehe ;)
Naja, hoffe das ist mit Ironie behaftet sonst hinkt der Vergleich schon arg.
Am Pi leuchtet kein Lämpchen, es qualmt nichts und es gibt auch erstmal keine Fehler.
Es kann lediglich passieren das unter bestimmten Konstellation die SD Karte einen Schaden nimmt.
Das passt zu deinem Auto Beispiel null.
@wendy2702 said in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Naja, hoffe das ist mit Ironie behaftet sonst hinkt der Vergleich schon arg.
Danke, war mir jetzt fast zu schnell aufgelöst... eigentlich wollte ich das @Jan1 überlassen.
:arrow_forward: Your mileage may vary :bulb:
:point_up:
Am Pi leuchtet kein Lämpchen, es qualmt nichts und es gibt auch erstmal keine Fehler.
Richtig, SD Karten haben (leider) kein SMART.. oder vielleicht die endurance/professional Versionen? Egal, die kosten mehr als ein Pi.
Es kann lediglich passieren das unter bestimmten Konstellation die SD Karte einen Schaden nimmt.
Flashzellen werden "verbraucht" bzw. "altern". Es ist lediglich die Frage "wie schnell". Hoher WAF = früher(er) Tot, so einfach die Rechnung.
-
@wendy2702 said in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Naja, hoffe das ist mit Ironie behaftet sonst hinkt der Vergleich schon arg.
Danke, war mir jetzt fast zu schnell aufgelöst... eigentlich wollte ich das @Jan1 überlassen.
:arrow_forward: Your mileage may vary :bulb:
:point_up:
Am Pi leuchtet kein Lämpchen, es qualmt nichts und es gibt auch erstmal keine Fehler.
Richtig, SD Karten haben (leider) kein SMART.. oder vielleicht die endurance/professional Versionen? Egal, die kosten mehr als ein Pi.
Es kann lediglich passieren das unter bestimmten Konstellation die SD Karte einen Schaden nimmt.
Flashzellen werden "verbraucht" bzw. "altern". Es ist lediglich die Frage "wie schnell". Hoher WAF = früher(er) Tot, so einfach die Rechnung.
@opensourcenomad
Das ist keine Ironie, sondern einfach sinnfrei.
Keine Fehler an der SD null Probleme und somit ist das Ding OK, was Deine Karre macht, ist schlicht Dein Problem ;)Wie ich schon geschrieben hatte, ich mag diese apokalyptischen Geschichten nicht, selbst wenn die durch Herstellerangaben untermauert sind. Um auf Deinen hinkenden Vergleich mit nem Auto zurück zukommen oder noch sinnfreier auf Lebensmittel. Es wird in der Regel angegeben, wie lange es mindestens halten sollte und nicht wie lange maximal und das trifft eben auch auf SD Karten zu, wobei einige eben meinen das trifft auch zu wenn sie darauf nem SWAP einrichten, oder sonstigen Blödsinn anstellen.
Edit:
können wird dann mal wieder zurück zum Thema hier?Edit 2:
Deiner eigener Link nach dem Du gefragt hast, alleine schon die Überschrift ist schon apokalyptisch und sehr gewagt. -
@opensourcenomad
Das ist keine Ironie, sondern einfach sinnfrei.
Keine Fehler an der SD null Probleme und somit ist das Ding OK, was Deine Karre macht, ist schlicht Dein Problem ;)Wie ich schon geschrieben hatte, ich mag diese apokalyptischen Geschichten nicht, selbst wenn die durch Herstellerangaben untermauert sind. Um auf Deinen hinkenden Vergleich mit nem Auto zurück zukommen oder noch sinnfreier auf Lebensmittel. Es wird in der Regel angegeben, wie lange es mindestens halten sollte und nicht wie lange maximal und das trifft eben auch auf SD Karten zu, wobei einige eben meinen das trifft auch zu wenn sie darauf nem SWAP einrichten, oder sonstigen Blödsinn anstellen.
Edit:
können wird dann mal wieder zurück zum Thema hier?Edit 2:
Deiner eigener Link nach dem Du gefragt hast, alleine schon die Überschrift ist schon apokalyptisch und sehr gewagt.@jan1 said in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
sondern einfach sinnfrei.
Genau darauf wollte ich hinaus! :muscle:
Genau wie deine Aussage "meine SD Karte hält schon zwei Jahre", selbst wenn du noch die Marke, Modell Größe und Produktionsdatum angeben würde ist das immer noch total Sinnfrei. Du hast eine individuelle "Schreiblast" auf deinem System die so niemand anders hat.
:arrow_forward: Your mileage may vary :bulb:
:point_up:
diese apokalyptischen Geschichten
Die will ich immer noch lesen, hast du einen Link?
durch Herstellerangaben untermauert
Ja, die ganzen Quellen/Nachweise sind echt schrecklich, wer soll den die ganzen Links öffnen... und auch noch lesen? Das wird echt zu viel... :nauseated_face:
wobei einige eben meinen das trifft auch zu wenn sie darauf nem SWAP einrichten
Die meisten machen das nicht selber, RaspberryOS macht das für einen :boom:
zurück zum Thema hier?
Unbedingt! Jetzt wo alles geklärt ist ;)
-
@jan1 said in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
sondern einfach sinnfrei.
Genau darauf wollte ich hinaus! :muscle:
Genau wie deine Aussage "meine SD Karte hält schon zwei Jahre", selbst wenn du noch die Marke, Modell Größe und Produktionsdatum angeben würde ist das immer noch total Sinnfrei. Du hast eine individuelle "Schreiblast" auf deinem System die so niemand anders hat.
:arrow_forward: Your mileage may vary :bulb:
:point_up:
diese apokalyptischen Geschichten
Die will ich immer noch lesen, hast du einen Link?
durch Herstellerangaben untermauert
Ja, die ganzen Quellen/Nachweise sind echt schrecklich, wer soll den die ganzen Links öffnen... und auch noch lesen? Das wird echt zu viel... :nauseated_face:
wobei einige eben meinen das trifft auch zu wenn sie darauf nem SWAP einrichten
Die meisten machen das nicht selber, RaspberryOS macht das für einen :boom:
zurück zum Thema hier?
Unbedingt! Jetzt wo alles geklärt ist ;)
-
@thomas-braun
Hi,
leider funktioniert es bei mir nicht. Kann es daran liegen das ich von einer SSD boote ?
Was bei mir noch kommt "Konfigurationsdateien bei diversen Paketen behalten werden sollten" und da habe ich mit "N" bestätigt. Wenn ich nachdem alles durchgelaufen ist neu boote ist der Raspberry nicht mehr erreichbar und er startet nicht. Nach kurzer Zeit verschwindet er auch in der Fritzbox. -
@thomas-braun
Hi,
leider funktioniert es bei mir nicht. Kann es daran liegen das ich von einer SSD boote ?
Was bei mir noch kommt "Konfigurationsdateien bei diversen Paketen behalten werden sollten" und da habe ich mit "N" bestätigt. Wenn ich nachdem alles durchgelaufen ist neu boote ist der Raspberry nicht mehr erreichbar und er startet nicht. Nach kurzer Zeit verschwindet er auch in der Fritzbox.@michael-schmitt
Möglich.
Der Bootvorgang läuft bei SSD anders ab. Da muss die entsprechende Datei belassen werden. -
@michael-schmitt
Möglich.
Der Bootvorgang läuft bei SSD anders ab. Da muss die entsprechende Datei belassen werden.@thomas-braun
ich habe noch ein wenig im Internet gesucht und nun läuft "Bullseye"
Das habe ich gemacht und nach dem reboot lief es. -
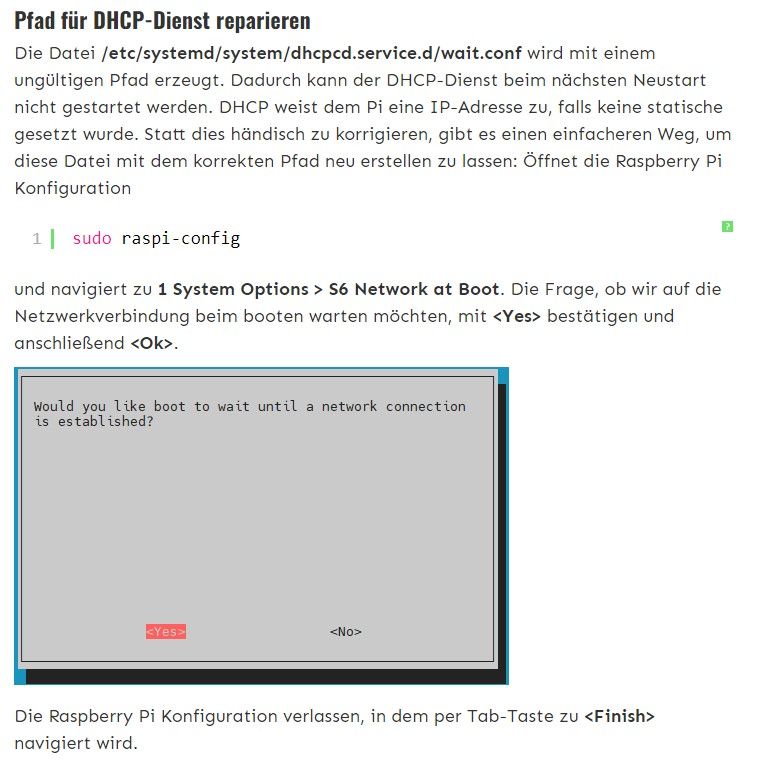
Hast du in raspi-config den Punkt auf 'warten' eingestellt?
1 System Options Configure system settings S6 Network at Boot Select wait for network connection on bootIch warte bei meinen Systemen nicht, deswegen gibt es bei mir auch die Datei nicht.
@thomas-braun Hi, super Anleitung. Hat gut funktioniert. Nach dem Reboot war der Raspi allerdings nicht mehr im Netzwerk. Durch Ändern der Wait Einstellung in der Raspi-Config, auf No, war er dann wieder im Netzwerk und alles läuft.
1 System Options Configure system settings S6 Network at Boot Select wait for network connection on bootDas Ändern der der Datei wait.conf, wie von einigen Usern beschrieben, hatte bei mir leider gar nichts gebracht.
Vielen Dank für deine tolle Anleitung und Unterstützung.
-
Hallo,
heute wollte ich mich aicu endlich mal am Update versuchen.
Leider scheitert das
sudo apt install gcc-8-baseirgendwie.
Er bleibt immer an der selben Stelle stehen.Last login: Fri Jul 15 08:57:28 2022 from 192.168.99.33 pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo apt full-upgrade Paketlisten werden gelesen... Fertig Abhängigkeitsbaum wird aufgebaut. Statusinformationen werden eingelesen.... Fertig Paketaktualisierung (Upgrade) wird berechnet... Fehler! Einige Pakete konnten nicht installiert werden. Das kann bedeuten, dass Sie eine unmögliche Situation angefordert haben oder, wenn Sie die Unstable-Distribution verwenden, dass einige erforderliche Pakete noch nicht erstellt wurden oder Incoming noch nicht verlassen haben. Die folgenden Informationen helfen Ihnen vielleicht, die Situation zu lösen: Die folgenden Pakete haben unerfüllte Abhängigkeiten: libc6-dev : Beschädigt: libgcc-8-dev (< 8.4.0-2~) aber 8.3.0-6+rpi1 soll installiert werden E: Fehler: Unterbrechungen durch pkgProblemResolver::Resolve hervorgerufen; dies könnte durch zurückgehaltene Pakete verursacht worden sein. pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo apt install gcc-8-base Paketlisten werden gelesen... Fertig Abhängigkeitsbaum wird aufgebaut. Statusinformationen werden eingelesen.... Fertig Die folgenden Pakete wurden automatisch installiert und werden nicht mehr benötigt: apt-show-versions dh-python geoclue-2.0 gir1.2-rsvg-2.0 icu-devtools iio-sensor-proxy libapt-pkg-perl libc-dev-bin libcairo-script-interpreter2 libcroco3 libffi-dev libfl2 libfribidi-dev libglib2.0-dev-bin libgraphite2-dev libgutenprint-common libgutenprint9 libharfbuzz-gobject0 libhiredis0.14 libice-dev libisl19 libjs-sphinxdoc libjs-underscore libkyotocabinet16v5 liblzo2-2 libmbim-glib4 libmbim-proxy libmemcached11 libmemcachedutil2 libmm-glib0 libpango-perl libpcre16-3 libpcre32-3 libpcrecpp0v5 libpixman-1-dev libpng-tools libpthread-stubs0-dev libpython2.7-minimal libqmi-glib5 libqmi-proxy libqt5positioning5 libqt5qml5 libqt5quick5 libqt5sensors5 libqt5webchannel5 libqt5webkit5 libqt5xmlpatterns5 libsepol1-dev libsm-dev libx11-dev libxau-dev libxcb-render0-dev libxcb-shm0-dev libxcb1-dev libxdmcp-dev libxext-dev libxrender-dev linux-libc-dev modemmanager pango1.0-tools printer-driver-gutenprint proftpd-doc python3.7 python3.7-minimal python3.7-venv x11proto-core-dev x11proto-dev x11proto-xext-dev xorg-sgml-doctools xtrans-dev Verwenden Sie »sudo apt autoremove«, um sie zu entfernen. Die folgenden zusätzlichen Pakete werden installiert: alacarte arandr binutils binutils-arm-linux-gnueabihf binutils-common clamtk cpp cpp-10 cpp-8 cups cups-client cups-common cups-core-drivers cups-daemon cups-ipp-utils cups-server-common edid-decode fio fontconfig-config fonts-urw-base35 gcc gcc-10 gcc-10-base gcc-8 gcc-9-base gir1.2-gdkpixbuf-2.0 gir1.2-harfbuzz-0.0 gir1.2-pango-1.0 gir1.2-rsvg-2.0 hardlink hplip hplip-data icu-devtools libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libapt-pkg-perl libapt-pkg6.0 libasan5 libasan6 libatomic1 libauthen-pam-perl libbinutils libblkid1 libbrotli1 libc-bin libc-dev-bin libc-l10n libc6 libc6-dbg libcairo-gobject-perl libcairo-gobject2 libcairo-perl libcairo-script-interpreter2 libcairo2 libcbor0 libcc1-0 libcommon-sense-perl libcrypt1 libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libcups2 libcupsimage2 libdbd-mysql-perl libdbi-perl libexpat1 libextutils-depends-perl libextutils-pkgconfig-perl libfcgi-perl libfcgi0ldbl libffi-dev libffi7 libfido2-1 libfile-fcntllock-perl libfontconfig1 libfreetype6 libgcc-10-dev libgcc-8-dev libgcc-s1 libgdk-pixbuf-2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf-xlib-2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-bin libgdk-pixbuf2.0-common libgfapi0 libgfortran5 libgfrpc0 libgfxdr0 libgirepository-1.0-1 libglib-object-introspection-perl libglib-perl libglib2.0-0 libglib2.0-bin libglib2.0-dev-bin libglusterfs0 libgnutls-dane0 libgnutls30 libgomp1 libgtk3-perl libharfbuzz-gobject0 libharfbuzz-icu0 libharfbuzz0b libhogweed6 libhpmud0 libhtml-parser-perl libicu67 libintl-perl libintl-xs-perl libio-pty-perl libisl23 libjson-xs-perl libldb2 liblocale-gettext-perl libmailutils7 libmount1 libmpdec3 libnet-ssleay-perl libnettle8 libnsl2 libp11-kit0 libpam0g libpango-1.0-0 libpango-perl libpangocairo-1.0-0 libpangoft2-1.0-0 libpangoxft-1.0-0 libpcre2-16-0 libpcre2-8-0 libpcre2-posix2 libperl5.32 libpng-tools libpng16-16 libproc-processtable-perl libpython3-stdlib libpython3.9 libpython3.9-minimal libpython3.9-stdlib libreadline8 librsvg2-2 librsvg2-common librtimulib-dev librtimulib-utils librtimulib7 libsane-hpaio libselinux1 libsepol1 libsepol1-dev libsmbclient libsnmp40 libstdc++6 libtalloc2 libtasn1-6 libtdb1 libterm-readkey-perl libtevent0 libtext-charwidth-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libtext-iconv-perl libtirpc-common libtirpc3 libubsan1 libwbclient0 libwebpmux3 libxxhash0 libzstd1 locales mailutils mailutils-common manpages manpages-dev mypy openssh-client openssh-server openssh-sftp-server perl perl-base perl-modules-5.32 printer-driver-hpcups python3 python3-apt python3-cairo python3-cffi-backend python3-crypto python3-cups python3-dbus python3-distro python3-distutils python3-gi python3-gi-cairo python3-lazy-object-proxy python3-ldb python3-lib2to3 python3-lxml python3-markupsafe python3-minimal python3-mypy python3-numpy python3-pil python3-psutil python3-pygame python3-renderpm python3-reportlab-accel python3-rpi.gpio python3-rtimulib python3-simplejson python3-smbc python3-smbus python3-spidev python3-talloc python3-tk python3-typed-ast python3-typing-extensions python3-venv python3-wrapt python3.9 python3.9-minimal python3.9-venv raspi-config rpi.gpio-common runit-helper samba-libs sense-hat zlib1g Vorgeschlagene Pakete: binutils-doc cabextract clamtk-gnome cpp-doc gcc-10-locales gcc-8-locales cups-bsd cups-pdf foomatic-db-compressed-ppds | foomatic-db smbclient gnuplot gfio python-scipy fonts-texgyre gcc-multilib autoconf automake libtool flex bison gcc-doc gcc-10-doc gcc-8-doc hplip-doc hplip-gui python3-notify2 glibc-doc libfont-freetype-perl libclone-perl libmldbm-perl libnet-daemon-perl libsql-statement-perl libxml-libxml-perl libxml2-utils dns-root-data gnutls-bin libpam-doc librsvg2-bin octave mailutils-mh mailutils-doc mypy-doc keychain libpam-ssh monkeysphere ssh-askpass molly-guard ufw perl-doc libterm-readline-gnu-perl | libterm-readline-perl-perl libtap-harness-archive-perl python3-doc python3-apt-dbg python-apt-doc python-dbus-doc python3-dbus-dbg python3-lxml-dbg python-lxml-doc gfortran python-numpy-doc python3-dev python3-numpy-dbg python3-pytest python-pil-doc python3-pil-dbg python-psutil-doc python-pygame-doc timidity python3-renderpm-dbg python-spidev-doc tix python3-tk-dbg python3.9-doc binfmt-support Empfohlene Pakete: ipp-usb libc6-dev | libc-dev libc6-dev apt libc-devtools libnss-nis libnss-nisplus libfcgi-bin Die folgenden Pakete werden ENTFERNT: build-essential g++ g++-8 libblkid-dev libc6-dev libcairo2-dev libexpat1-dev libfontconfig1-dev libfreetype6-dev libgcc1 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-dev libglib2.0-dev libgtk2-perl libharfbuzz-dev libicu-dev libjpeg-dev libjpeg62-turbo-dev libldb1 libmailutils5 libmount-dev libpam0g-dev libpango1.0-dev libpcre2-posix0 libpcre3-dev libpng-dev libpython-all-dev libpython-dev libpython-stdlib libpython2-dev libpython2-stdlib libpython2.7 libpython2.7-dev libpython2.7-stdlib libpython3-dev libpython3.7-dev librsvg2-dev libselinux1-dev libstdc++-8-dev libxft-dev python python-all python-all-dev python-asn1crypto python-automationhat python-blinker python-blinkt python-buttonshim python-cairo python-cap1xxx python-certifi python-cffi-backend python-chardet python-click python-colorama python-colorzero python-configparser python-cookies python-crypto python-cryptography python-dbus python-dev python-drumhat python-entrypoints python-enum34 python-envirophat python-explorerhat python-flask python-fourletterphat python-funcsigs python-gi python-gobject-2 python-gpiozero python-gtk2 python-idna python-ipaddress python-itsdangerous python-jinja2 python-jwt python-keyring python-keyrings.alt python-markupsafe python-microdotphat python-minimal python-mock python-mote python-motephat python-numpy python-oauthlib python-olefile python-openssl python-pantilthat python-pbr python-phatbeat python-pianohat python-picamera python-piglow python-pigpio python-pil python-pip python-pkg-resources python-pygame python-pyinotify python-rainbowhat python-requests python-requests-oauthlib python-responses python-rpi.gpio python-rtimulib python-scrollphat python-scrollphathd python-secretstorage python-sense-hat python-serial python-setuptools python-simplejson python-six python-skywriter python-smbus python-sn3218 python-spidev python-talloc python-tk python-touchphat python-twython python-unicornhathd python-urllib3 python-werkzeug python-wheel python-xdg python2 python2-dev python2-minimal python2.7 python2.7-dev python2.7-minimal python3-dev python3.7-dev uuid-dev zlib1g-dev Die folgenden NEUEN Pakete werden installiert: cpp-10 edid-decode fonts-urw-base35 gcc-10 gcc-10-base gcc-9-base libapt-pkg6.0 libasan6 libcairo-gobject-perl libcbor0 libcrypt1 libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libextutils-depends-perl libextutils-pkgconfig-perl libfcgi0ldbl libffi7 libfido2-1 libgcc-10-dev libgcc-s1 libgdk-pixbuf-2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf-xlib-2.0-0 libglib-object-introspection-perl libgtk3-perl libhogweed6 libicu67 libisl23 libldb2 libmailutils7 libmpdec3 libnettle8 libnsl2 libpcre2-posix2 libperl5.32 libpython3.9 libpython3.9-minimal libpython3.9-stdlib libreadline8 libsnmp40 libxxhash0 perl-modules-5.32 python3-distro python3-gi-cairo python3-ldb python3-talloc python3-typing-extensions python3.9 python3.9-minimal python3.9-venv runit-helper Die folgenden Pakete werden aktualisiert (Upgrade): alacarte arandr binutils binutils-arm-linux-gnueabihf binutils-common clamtk cpp cpp-8 cups cups-client cups-common cups-core-drivers cups-daemon cups-ipp-utils cups-server-common fio fontconfig-config gcc gcc-8 gcc-8-base gir1.2-gdkpixbuf-2.0 gir1.2-harfbuzz-0.0 gir1.2-pango-1.0 gir1.2-rsvg-2.0 hardlink hplip hplip-data icu-devtools libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libapt-pkg-perl libasan5 libatomic1 libauthen-pam-perl libbinutils libblkid1 libbrotli1 libc-bin libc-dev-bin libc-l10n libc6 libc6-dbg libcairo-gobject2 libcairo-perl libcairo-script-interpreter2 libcairo2 libcc1-0 libcommon-sense-perl libcups2 libcupsimage2 libdbd-mysql-perl libdbi-perl libexpat1 libfcgi-perl libffi-dev libfile-fcntllock-perl libfontconfig1 libfreetype6 libgcc-8-dev libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-bin libgdk-pixbuf2.0-common libgfapi0 libgfortran5 libgfrpc0 libgfxdr0 libgirepository-1.0-1 libglib-perl libglib2.0-0 libglib2.0-bin libglib2.0-dev-bin libglusterfs0 libgnutls-dane0 libgnutls30 libgomp1 libharfbuzz-gobject0 libharfbuzz-icu0 libharfbuzz0b libhpmud0 libhtml-parser-perl libintl-perl libintl-xs-perl libio-pty-perl libjson-xs-perl liblocale-gettext-perl libmount1 libnet-ssleay-perl libp11-kit0 libpam0g libpango-1.0-0 libpango-perl libpangocairo-1.0-0 libpangoft2-1.0-0 libpangoxft-1.0-0 libpcre2-16-0 libpcre2-8-0 libpng-tools libpng16-16 libproc-processtable-perl libpython3-stdlib librsvg2-2 librsvg2-common librtimulib-dev librtimulib-utils librtimulib7 libsane-hpaio libselinux1 libsepol1 libsepol1-dev libsmbclient libstdc++6 libtalloc2 libtasn1-6 libtdb1 libterm-readkey-perl libtevent0 libtext-charwidth-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libtext-iconv-perl libtirpc-common libtirpc3 libubsan1 libwbclient0 libwebpmux3 libzstd1 locales mailutils mailutils-common manpages manpages-dev mypy openssh-client openssh-server openssh-sftp-server perl perl-base printer-driver-hpcups python3 python3-apt python3-cairo python3-cffi-backend python3-crypto python3-cups python3-dbus python3-distutils python3-gi python3-lazy-object-proxy python3-lib2to3 python3-lxml python3-markupsafe python3-minimal python3-mypy python3-numpy python3-pil python3-psutil python3-pygame python3-renderpm python3-reportlab-accel python3-rpi.gpio python3-rtimulib python3-simplejson python3-smbc python3-smbus python3-spidev python3-tk python3-typed-ast python3-venv python3-wrapt raspi-config rpi.gpio-common samba-libs sense-hat zlib1g 172 aktualisiert, 50 neu installiert, 139 zu entfernen und 1070 nicht aktualisiert. Es müssen noch 0 B von 162 MB an Archiven heruntergeladen werden. Nach dieser Operation werden 51,1 MB Plattenplatz freigegeben. Möchten Sie fortfahren? [J/n] j Changelogs werden gelesen... Fertig apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt (2.1.16) unstable; urgency=medium Automatically remove unused kernels on apt {dist,full}-upgrade. To revert to previous behavior, set APT::Get::AutomaticRemove::Kernels to false or pass --no-auto-remove to the command. apt-get remains unchanged. Packages files can now set the Phased-Update-Percentage field to restrict update rollout to a specified percentage of machines. Previously, this has only been available to users of Ubuntu's update-manager tool. See apt_preferences(5) for details and how to configure multiple systems to get apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt (2.1.16) unstable; urgency=medium Automatically remove unused kernels on apt {dist,full}-upgrade. To revert to previous behavior, set APT::Get::AutomaticRemove::Kernels to false or pass --no-auto-remove to the command. apt-get remains unchanged. Packages files can now set the Phased-Update-Percentage field to restrict update rollout to a specified percentage of machines. Previously, this has only been available to users of Ubuntu's update-manager tool. See apt_preferences(5) for details and how to configure multiple systems to get the same updates. Phased updates are disabled in chroots for now to not break buildd-style setups. -- Julian Andres Klode <jak@debian.org> Fri, 08 Jan 2021 22:01:50 +0100 -
Hallo,
heute wollte ich mich aicu endlich mal am Update versuchen.
Leider scheitert das
sudo apt install gcc-8-baseirgendwie.
Er bleibt immer an der selben Stelle stehen.Last login: Fri Jul 15 08:57:28 2022 from 192.168.99.33 pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo apt full-upgrade Paketlisten werden gelesen... Fertig Abhängigkeitsbaum wird aufgebaut. Statusinformationen werden eingelesen.... Fertig Paketaktualisierung (Upgrade) wird berechnet... Fehler! Einige Pakete konnten nicht installiert werden. Das kann bedeuten, dass Sie eine unmögliche Situation angefordert haben oder, wenn Sie die Unstable-Distribution verwenden, dass einige erforderliche Pakete noch nicht erstellt wurden oder Incoming noch nicht verlassen haben. Die folgenden Informationen helfen Ihnen vielleicht, die Situation zu lösen: Die folgenden Pakete haben unerfüllte Abhängigkeiten: libc6-dev : Beschädigt: libgcc-8-dev (< 8.4.0-2~) aber 8.3.0-6+rpi1 soll installiert werden E: Fehler: Unterbrechungen durch pkgProblemResolver::Resolve hervorgerufen; dies könnte durch zurückgehaltene Pakete verursacht worden sein. pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo apt install gcc-8-base Paketlisten werden gelesen... Fertig Abhängigkeitsbaum wird aufgebaut. Statusinformationen werden eingelesen.... Fertig Die folgenden Pakete wurden automatisch installiert und werden nicht mehr benötigt: apt-show-versions dh-python geoclue-2.0 gir1.2-rsvg-2.0 icu-devtools iio-sensor-proxy libapt-pkg-perl libc-dev-bin libcairo-script-interpreter2 libcroco3 libffi-dev libfl2 libfribidi-dev libglib2.0-dev-bin libgraphite2-dev libgutenprint-common libgutenprint9 libharfbuzz-gobject0 libhiredis0.14 libice-dev libisl19 libjs-sphinxdoc libjs-underscore libkyotocabinet16v5 liblzo2-2 libmbim-glib4 libmbim-proxy libmemcached11 libmemcachedutil2 libmm-glib0 libpango-perl libpcre16-3 libpcre32-3 libpcrecpp0v5 libpixman-1-dev libpng-tools libpthread-stubs0-dev libpython2.7-minimal libqmi-glib5 libqmi-proxy libqt5positioning5 libqt5qml5 libqt5quick5 libqt5sensors5 libqt5webchannel5 libqt5webkit5 libqt5xmlpatterns5 libsepol1-dev libsm-dev libx11-dev libxau-dev libxcb-render0-dev libxcb-shm0-dev libxcb1-dev libxdmcp-dev libxext-dev libxrender-dev linux-libc-dev modemmanager pango1.0-tools printer-driver-gutenprint proftpd-doc python3.7 python3.7-minimal python3.7-venv x11proto-core-dev x11proto-dev x11proto-xext-dev xorg-sgml-doctools xtrans-dev Verwenden Sie »sudo apt autoremove«, um sie zu entfernen. Die folgenden zusätzlichen Pakete werden installiert: alacarte arandr binutils binutils-arm-linux-gnueabihf binutils-common clamtk cpp cpp-10 cpp-8 cups cups-client cups-common cups-core-drivers cups-daemon cups-ipp-utils cups-server-common edid-decode fio fontconfig-config fonts-urw-base35 gcc gcc-10 gcc-10-base gcc-8 gcc-9-base gir1.2-gdkpixbuf-2.0 gir1.2-harfbuzz-0.0 gir1.2-pango-1.0 gir1.2-rsvg-2.0 hardlink hplip hplip-data icu-devtools libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libapt-pkg-perl libapt-pkg6.0 libasan5 libasan6 libatomic1 libauthen-pam-perl libbinutils libblkid1 libbrotli1 libc-bin libc-dev-bin libc-l10n libc6 libc6-dbg libcairo-gobject-perl libcairo-gobject2 libcairo-perl libcairo-script-interpreter2 libcairo2 libcbor0 libcc1-0 libcommon-sense-perl libcrypt1 libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libcups2 libcupsimage2 libdbd-mysql-perl libdbi-perl libexpat1 libextutils-depends-perl libextutils-pkgconfig-perl libfcgi-perl libfcgi0ldbl libffi-dev libffi7 libfido2-1 libfile-fcntllock-perl libfontconfig1 libfreetype6 libgcc-10-dev libgcc-8-dev libgcc-s1 libgdk-pixbuf-2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf-xlib-2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-bin libgdk-pixbuf2.0-common libgfapi0 libgfortran5 libgfrpc0 libgfxdr0 libgirepository-1.0-1 libglib-object-introspection-perl libglib-perl libglib2.0-0 libglib2.0-bin libglib2.0-dev-bin libglusterfs0 libgnutls-dane0 libgnutls30 libgomp1 libgtk3-perl libharfbuzz-gobject0 libharfbuzz-icu0 libharfbuzz0b libhogweed6 libhpmud0 libhtml-parser-perl libicu67 libintl-perl libintl-xs-perl libio-pty-perl libisl23 libjson-xs-perl libldb2 liblocale-gettext-perl libmailutils7 libmount1 libmpdec3 libnet-ssleay-perl libnettle8 libnsl2 libp11-kit0 libpam0g libpango-1.0-0 libpango-perl libpangocairo-1.0-0 libpangoft2-1.0-0 libpangoxft-1.0-0 libpcre2-16-0 libpcre2-8-0 libpcre2-posix2 libperl5.32 libpng-tools libpng16-16 libproc-processtable-perl libpython3-stdlib libpython3.9 libpython3.9-minimal libpython3.9-stdlib libreadline8 librsvg2-2 librsvg2-common librtimulib-dev librtimulib-utils librtimulib7 libsane-hpaio libselinux1 libsepol1 libsepol1-dev libsmbclient libsnmp40 libstdc++6 libtalloc2 libtasn1-6 libtdb1 libterm-readkey-perl libtevent0 libtext-charwidth-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libtext-iconv-perl libtirpc-common libtirpc3 libubsan1 libwbclient0 libwebpmux3 libxxhash0 libzstd1 locales mailutils mailutils-common manpages manpages-dev mypy openssh-client openssh-server openssh-sftp-server perl perl-base perl-modules-5.32 printer-driver-hpcups python3 python3-apt python3-cairo python3-cffi-backend python3-crypto python3-cups python3-dbus python3-distro python3-distutils python3-gi python3-gi-cairo python3-lazy-object-proxy python3-ldb python3-lib2to3 python3-lxml python3-markupsafe python3-minimal python3-mypy python3-numpy python3-pil python3-psutil python3-pygame python3-renderpm python3-reportlab-accel python3-rpi.gpio python3-rtimulib python3-simplejson python3-smbc python3-smbus python3-spidev python3-talloc python3-tk python3-typed-ast python3-typing-extensions python3-venv python3-wrapt python3.9 python3.9-minimal python3.9-venv raspi-config rpi.gpio-common runit-helper samba-libs sense-hat zlib1g Vorgeschlagene Pakete: binutils-doc cabextract clamtk-gnome cpp-doc gcc-10-locales gcc-8-locales cups-bsd cups-pdf foomatic-db-compressed-ppds | foomatic-db smbclient gnuplot gfio python-scipy fonts-texgyre gcc-multilib autoconf automake libtool flex bison gcc-doc gcc-10-doc gcc-8-doc hplip-doc hplip-gui python3-notify2 glibc-doc libfont-freetype-perl libclone-perl libmldbm-perl libnet-daemon-perl libsql-statement-perl libxml-libxml-perl libxml2-utils dns-root-data gnutls-bin libpam-doc librsvg2-bin octave mailutils-mh mailutils-doc mypy-doc keychain libpam-ssh monkeysphere ssh-askpass molly-guard ufw perl-doc libterm-readline-gnu-perl | libterm-readline-perl-perl libtap-harness-archive-perl python3-doc python3-apt-dbg python-apt-doc python-dbus-doc python3-dbus-dbg python3-lxml-dbg python-lxml-doc gfortran python-numpy-doc python3-dev python3-numpy-dbg python3-pytest python-pil-doc python3-pil-dbg python-psutil-doc python-pygame-doc timidity python3-renderpm-dbg python-spidev-doc tix python3-tk-dbg python3.9-doc binfmt-support Empfohlene Pakete: ipp-usb libc6-dev | libc-dev libc6-dev apt libc-devtools libnss-nis libnss-nisplus libfcgi-bin Die folgenden Pakete werden ENTFERNT: build-essential g++ g++-8 libblkid-dev libc6-dev libcairo2-dev libexpat1-dev libfontconfig1-dev libfreetype6-dev libgcc1 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-dev libglib2.0-dev libgtk2-perl libharfbuzz-dev libicu-dev libjpeg-dev libjpeg62-turbo-dev libldb1 libmailutils5 libmount-dev libpam0g-dev libpango1.0-dev libpcre2-posix0 libpcre3-dev libpng-dev libpython-all-dev libpython-dev libpython-stdlib libpython2-dev libpython2-stdlib libpython2.7 libpython2.7-dev libpython2.7-stdlib libpython3-dev libpython3.7-dev librsvg2-dev libselinux1-dev libstdc++-8-dev libxft-dev python python-all python-all-dev python-asn1crypto python-automationhat python-blinker python-blinkt python-buttonshim python-cairo python-cap1xxx python-certifi python-cffi-backend python-chardet python-click python-colorama python-colorzero python-configparser python-cookies python-crypto python-cryptography python-dbus python-dev python-drumhat python-entrypoints python-enum34 python-envirophat python-explorerhat python-flask python-fourletterphat python-funcsigs python-gi python-gobject-2 python-gpiozero python-gtk2 python-idna python-ipaddress python-itsdangerous python-jinja2 python-jwt python-keyring python-keyrings.alt python-markupsafe python-microdotphat python-minimal python-mock python-mote python-motephat python-numpy python-oauthlib python-olefile python-openssl python-pantilthat python-pbr python-phatbeat python-pianohat python-picamera python-piglow python-pigpio python-pil python-pip python-pkg-resources python-pygame python-pyinotify python-rainbowhat python-requests python-requests-oauthlib python-responses python-rpi.gpio python-rtimulib python-scrollphat python-scrollphathd python-secretstorage python-sense-hat python-serial python-setuptools python-simplejson python-six python-skywriter python-smbus python-sn3218 python-spidev python-talloc python-tk python-touchphat python-twython python-unicornhathd python-urllib3 python-werkzeug python-wheel python-xdg python2 python2-dev python2-minimal python2.7 python2.7-dev python2.7-minimal python3-dev python3.7-dev uuid-dev zlib1g-dev Die folgenden NEUEN Pakete werden installiert: cpp-10 edid-decode fonts-urw-base35 gcc-10 gcc-10-base gcc-9-base libapt-pkg6.0 libasan6 libcairo-gobject-perl libcbor0 libcrypt1 libctf-nobfd0 libctf0 libextutils-depends-perl libextutils-pkgconfig-perl libfcgi0ldbl libffi7 libfido2-1 libgcc-10-dev libgcc-s1 libgdk-pixbuf-2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf-xlib-2.0-0 libglib-object-introspection-perl libgtk3-perl libhogweed6 libicu67 libisl23 libldb2 libmailutils7 libmpdec3 libnettle8 libnsl2 libpcre2-posix2 libperl5.32 libpython3.9 libpython3.9-minimal libpython3.9-stdlib libreadline8 libsnmp40 libxxhash0 perl-modules-5.32 python3-distro python3-gi-cairo python3-ldb python3-talloc python3-typing-extensions python3.9 python3.9-minimal python3.9-venv runit-helper Die folgenden Pakete werden aktualisiert (Upgrade): alacarte arandr binutils binutils-arm-linux-gnueabihf binutils-common clamtk cpp cpp-8 cups cups-client cups-common cups-core-drivers cups-daemon cups-ipp-utils cups-server-common fio fontconfig-config gcc gcc-8 gcc-8-base gir1.2-gdkpixbuf-2.0 gir1.2-harfbuzz-0.0 gir1.2-pango-1.0 gir1.2-rsvg-2.0 hardlink hplip hplip-data icu-devtools libalgorithm-diff-xs-perl libapt-pkg-perl libasan5 libatomic1 libauthen-pam-perl libbinutils libblkid1 libbrotli1 libc-bin libc-dev-bin libc-l10n libc6 libc6-dbg libcairo-gobject2 libcairo-perl libcairo-script-interpreter2 libcairo2 libcc1-0 libcommon-sense-perl libcups2 libcupsimage2 libdbd-mysql-perl libdbi-perl libexpat1 libfcgi-perl libffi-dev libfile-fcntllock-perl libfontconfig1 libfreetype6 libgcc-8-dev libgdk-pixbuf2.0-0 libgdk-pixbuf2.0-bin libgdk-pixbuf2.0-common libgfapi0 libgfortran5 libgfrpc0 libgfxdr0 libgirepository-1.0-1 libglib-perl libglib2.0-0 libglib2.0-bin libglib2.0-dev-bin libglusterfs0 libgnutls-dane0 libgnutls30 libgomp1 libharfbuzz-gobject0 libharfbuzz-icu0 libharfbuzz0b libhpmud0 libhtml-parser-perl libintl-perl libintl-xs-perl libio-pty-perl libjson-xs-perl liblocale-gettext-perl libmount1 libnet-ssleay-perl libp11-kit0 libpam0g libpango-1.0-0 libpango-perl libpangocairo-1.0-0 libpangoft2-1.0-0 libpangoxft-1.0-0 libpcre2-16-0 libpcre2-8-0 libpng-tools libpng16-16 libproc-processtable-perl libpython3-stdlib librsvg2-2 librsvg2-common librtimulib-dev librtimulib-utils librtimulib7 libsane-hpaio libselinux1 libsepol1 libsepol1-dev libsmbclient libstdc++6 libtalloc2 libtasn1-6 libtdb1 libterm-readkey-perl libtevent0 libtext-charwidth-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libtext-iconv-perl libtirpc-common libtirpc3 libubsan1 libwbclient0 libwebpmux3 libzstd1 locales mailutils mailutils-common manpages manpages-dev mypy openssh-client openssh-server openssh-sftp-server perl perl-base printer-driver-hpcups python3 python3-apt python3-cairo python3-cffi-backend python3-crypto python3-cups python3-dbus python3-distutils python3-gi python3-lazy-object-proxy python3-lib2to3 python3-lxml python3-markupsafe python3-minimal python3-mypy python3-numpy python3-pil python3-psutil python3-pygame python3-renderpm python3-reportlab-accel python3-rpi.gpio python3-rtimulib python3-simplejson python3-smbc python3-smbus python3-spidev python3-tk python3-typed-ast python3-venv python3-wrapt raspi-config rpi.gpio-common samba-libs sense-hat zlib1g 172 aktualisiert, 50 neu installiert, 139 zu entfernen und 1070 nicht aktualisiert. Es müssen noch 0 B von 162 MB an Archiven heruntergeladen werden. Nach dieser Operation werden 51,1 MB Plattenplatz freigegeben. Möchten Sie fortfahren? [J/n] j Changelogs werden gelesen... Fertig apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt (2.1.16) unstable; urgency=medium Automatically remove unused kernels on apt {dist,full}-upgrade. To revert to previous behavior, set APT::Get::AutomaticRemove::Kernels to false or pass --no-auto-remove to the command. apt-get remains unchanged. Packages files can now set the Phased-Update-Percentage field to restrict update rollout to a specified percentage of machines. Previously, this has only been available to users of Ubuntu's update-manager tool. See apt_preferences(5) for details and how to configure multiple systems to get apt-listchanges: Neuigkeiten ---------------------------- apt (2.1.16) unstable; urgency=medium Automatically remove unused kernels on apt {dist,full}-upgrade. To revert to previous behavior, set APT::Get::AutomaticRemove::Kernels to false or pass --no-auto-remove to the command. apt-get remains unchanged. Packages files can now set the Phased-Update-Percentage field to restrict update rollout to a specified percentage of machines. Previously, this has only been available to users of Ubuntu's update-manager tool. See apt_preferences(5) for details and how to configure multiple systems to get the same updates. Phased updates are disabled in chroots for now to not break buildd-style setups. -- Julian Andres Klode <jak@debian.org> Fri, 08 Jan 2021 22:01:50 +0100@david-g
Wie ist der jetzige Stand?
uname -m && whoami && pwd && sudo apt update &> /dev/null && sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-dev -
@david-g
Wie ist der jetzige Stand?
uname -m && whoami && pwd && sudo apt update &> /dev/null && sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-devpi@iobroker:~ $ uname -m && whoami && pwd && sudo apt update &> /dev/null && sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-dev armv7l pi /home/pi -
pi@iobroker:~ $ uname -m && whoami && pwd && sudo apt update &> /dev/null && sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-dev armv7l pi /home/pi@david-g sagte in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Dann anders...sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-devUnd von welcher Version aus machst du den Sprung auf Bullseye?
-
@david-g sagte in Upgrade von Debian 10 'Buster' auf 11 'Bullseye':
Dann anders...sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-devUnd von welcher Version aus machst du den Sprung auf Bullseye?
pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-dev OK:1 http://raspbian.raspberrypi.org/raspbian bullseye InRelease OK:2 http://archive.raspberrypi.org/debian bullseye InRelease OK:3 https://deb.nodesource.com/node_16.x bullseye InRelease Paketlisten werden gelesen... Fertig Abhängigkeitsbaum wird aufgebaut. Statusinformationen werden eingelesen.... Fertig Aktualisierung für 1290 Pakete verfügbar. Führen Sie »apt list --upgradable« aus, um sie anzuzeigen. libc6-dev: Installiert: 2.28-10+rpt2+rpi1+deb10u1 Installationskandidat: 2.31-13+rpt2+rpi1+deb11u3 Versionstabelle: 2.31-13+rpt2+rpi1+deb11u3 500 500 http://archive.raspberrypi.org/debian bullseye/main armhf Packages 2.31-13+rpi1+deb11u3 500 500 http://raspbian.raspberrypi.org/raspbian bullseye/main armhf Packages *** 2.28-10+rpt2+rpi1+deb10u1 100 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status libgcc-8-dev: Installiert: 8.3.0-6+rpi1 Installationskandidat: 8.4.0-7+rpi1 Versionstabelle: 8.4.0-7+rpi1 500 500 http://raspbian.raspberrypi.org/raspbian bullseye/main armhf Packages *** 8.3.0-6+rpi1 100 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status pi@iobroker:~ $Komme von buster.
-
pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo apt update && apt policy libc6-dev libgcc-8-dev OK:1 http://raspbian.raspberrypi.org/raspbian bullseye InRelease OK:2 http://archive.raspberrypi.org/debian bullseye InRelease OK:3 https://deb.nodesource.com/node_16.x bullseye InRelease Paketlisten werden gelesen... Fertig Abhängigkeitsbaum wird aufgebaut. Statusinformationen werden eingelesen.... Fertig Aktualisierung für 1290 Pakete verfügbar. Führen Sie »apt list --upgradable« aus, um sie anzuzeigen. libc6-dev: Installiert: 2.28-10+rpt2+rpi1+deb10u1 Installationskandidat: 2.31-13+rpt2+rpi1+deb11u3 Versionstabelle: 2.31-13+rpt2+rpi1+deb11u3 500 500 http://archive.raspberrypi.org/debian bullseye/main armhf Packages 2.31-13+rpi1+deb11u3 500 500 http://raspbian.raspberrypi.org/raspbian bullseye/main armhf Packages *** 2.28-10+rpt2+rpi1+deb10u1 100 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status libgcc-8-dev: Installiert: 8.3.0-6+rpi1 Installationskandidat: 8.4.0-7+rpi1 Versionstabelle: 8.4.0-7+rpi1 500 500 http://raspbian.raspberrypi.org/raspbian bullseye/main armhf Packages *** 8.3.0-6+rpi1 100 100 /var/lib/dpkg/status pi@iobroker:~ $Komme von buster.
@david-g
MIt gcc und Konsorten würde ich nicht rumfrickeln.
Installier Bullseye neu. -
@david-g
MIt gcc und Konsorten würde ich nicht rumfrickeln.
Installier Bullseye neu.Da komme ich die nächste Zeit nicht zu.
SQL und nut müssen dann auch neu installiert werden. Nut war ein Krampf....Weist du, wie ich
sudo sed -i 's/bullseye\/updates/bullseye-security/g' /etc/apt/sources.list sudo sed -i 's/buster/bullseye/g' /etc/apt/sources.list sudo sed -i 's/buster/bullseye/g' /etc/apt/Anpassen muss um erstmal wieder auf Buster zu kommen?
-
Da komme ich die nächste Zeit nicht zu.
SQL und nut müssen dann auch neu installiert werden. Nut war ein Krampf....Weist du, wie ich
sudo sed -i 's/bullseye\/updates/bullseye-security/g' /etc/apt/sources.list sudo sed -i 's/buster/bullseye/g' /etc/apt/sources.list sudo sed -i 's/buster/bullseye/g' /etc/apt/Anpassen muss um erstmal wieder auf Buster zu kommen?
@david-g
Buster erreicht in wenigen Wochen sein EndOfLife.
Die sed Befehle: Einfach buster durch bullseye ersetzen und umgekehrt.
-
@david-g
Buster erreicht in wenigen Wochen sein EndOfLife.
Die sed Befehle: Einfach buster durch bullseye ersetzen und umgekehrt.
Dann wirds langsam Zeit......
Gibt's kein Betriebssystem was sich empfiehlt, was nicht diese Hauptversionen hat und einfach durch Updates aktuell bleibt?Die letzte Zeile möchte er nicht:
pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo sed -i 's/buster\/updates/buster-security/g' /etc/apt/sources.list pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo sed -i 's/bullseye/buster/g' /etc/apt/sources.list pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo sed -i 's/bullseye/buster/g' /etc/apt/ sed: /etc/apt/ kann nicht bearbeitet werden: Das ist keine normale Datei pi@iobroker:~ $Edit:
Da fällt mir grad ein Artikel ein, den ich heute morgen gelesen habe.Ist was der Grund für den Wechsel bei Google? So verstehe ich es im Artikel
https://www.heise.de/news/Google-Warum-uns-Ubuntu-zu-traege-war-und-wie-wir-jetzt-gLinux-administrieren-7179099.html -
Dann wirds langsam Zeit......
Gibt's kein Betriebssystem was sich empfiehlt, was nicht diese Hauptversionen hat und einfach durch Updates aktuell bleibt?Die letzte Zeile möchte er nicht:
pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo sed -i 's/buster\/updates/buster-security/g' /etc/apt/sources.list pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo sed -i 's/bullseye/buster/g' /etc/apt/sources.list pi@iobroker:~ $ sudo sed -i 's/bullseye/buster/g' /etc/apt/ sed: /etc/apt/ kann nicht bearbeitet werden: Das ist keine normale Datei pi@iobroker:~ $Edit:
Da fällt mir grad ein Artikel ein, den ich heute morgen gelesen habe.Ist was der Grund für den Wechsel bei Google? So verstehe ich es im Artikel
https://www.heise.de/news/Google-Warum-uns-Ubuntu-zu-traege-war-und-wie-wir-jetzt-gLinux-administrieren-7179099.html@david-g
sudo sed -i 's/bullseye/buster/g' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/*Es gibt sog. 'rolling releases', auch Debian 'sid' wäre sowas ähnliches.
Die sind aber in der Pflege aufwändiger als Distributionen mit festen Releases.Die Übergangsfrist von einem Jahr von Release zu Releases sind bei Debian aber eigentlich ausreichend groß, um da nicht auf den letzten Drücker (oder gar erst nach dem Ableben der Version) hektisch werden zu müssen.


